STRUCTURE OF BUSINESS:
The structure of business refers to the components and parts of business comprising different classes of activities that it exercises. Business activities can be greatly classified in three classes they are as follows:industry,commerce and services.



INDUSTRY:
Industry refers to the production of goods through the utilization of various resources available in surroundings. Industry is the process of extracting production ,conversion, and fabrication of products by the use of human skills and mechanical power.
Industrial products are those used for further production of products. similarly, the goods used for further processing are called intermediate products such as semi-processed products.
Types of Industry
Generally, the industry is classified into two broad parts they are as follows:
Primary industry:
Primary industry is the basic industry whereby natural resources are consumed and living organisms and plants are reproduced. The role of nature is important in primary industry. The products of such industry are used by the secondary types of industry.

-Extractive industries: This type of industries are extractive from the nature like air, sea, earth, and soil with little application of human skills. Example of such industries are mining of gold and cold from the earth. fishing from sea or rivers, exaction of oil and gas from the oil wells risings crops from soil and climate and more.
Geneti c industries:the industries in which certain sp
c industries:the industries in which certain sp ecies of plants and animals are multiplied and reproduction for the purpose of creating of wealth is called genetic industries.some of the examples are as follows of genetic industries poultry farming; plants grown for sale; animal husbandry where cattle are raised for milk and leather and sheep's; orchards to harvest different kinds of fruits; commercial kennels and agriculture
ecies of plants and animals are multiplied and reproduction for the purpose of creating of wealth is called genetic industries.some of the examples are as follows of genetic industries poultry farming; plants grown for sale; animal husbandry where cattle are raised for milk and leather and sheep's; orchards to harvest different kinds of fruits; commercial kennels and agriculture
Secondary Industries:
The Industries are which convert the raw materials and semi-processed materials into finished goods is known as Secondary industries. Secondary industries depends upon the outputs of the basic industries. Secondary industries can be categories into manufacturing and construction.
can be categories into manufacturing and construction.
Manufacturing industries:Manufacturing industries transform or convert raw materials into finished products. these industries create a from utility by converting raw materials into final products. Manufacturing industries example are iron and steel,automobile, machinery,electrical and electronics,sugar mills, textile mills, mechanical, etc.
Manufacturing industries is also divided into sub-parts they are as below:
Analytical industries: The industries which utilize analytic process in the
production of goods. Goods and services are manufactured by analyzing the raw materials and separates them to give or produce final products. for example;oils refineries which produces kerosene, diesel, aviation oil, petrol and lubricating.
Synthetic industries: Synthetic industries' are those type of production which uses synthetic while producing goods and final products. for example:- mixing of limestone,coal,clay,gypsum to formed cement.
which uses synthetic while producing goods and final products. for example:- mixing of limestone,coal,clay,gypsum to formed cement.
Processing industries: such types of industries, raw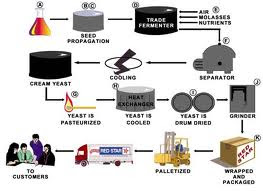
materials are processed through different phase of production to attend final products. the example of such industries is the raw jute passes through different stages of spinning, weaving, sewing and dyeing to produce jute products.
Assembling Industries:Assembling Industries are such industries where different components or parts
such industries where different components or parts
already manufactured by other companies and are
brought together and assemble to produce a final products.
for example automobile, radio, bicycle, watch,
computers,televisions.
continuous Industries: In such type of industries, all the needed
materials are insert into the machine at one point from which successive are automatically performed to turn them into a finished products. for example; Bhirkuti paper mill, Butwal spinning mill, lumbini sugar mill are the example of Nepal for continues types of manufacturing industries.
Construction Industries: The construction industries which are
involved in the construction of roads, bridges,culverts, building,
culverts and so on. for example such construction takes place at a
fixed site. Construction industries are of cement, concretes, steels,
irons and tar coal as raw materials.

COMMERCE: The process of exchanging goods and services is known as commerce.
In the words of James Stephenson,"Commerce is concerned with the exchange of goods with all that is involved in buying and selling of goods at any stage in their progress from raw materials to finished goods in the consumers' hands. It covers not only the function of buying ans selling and handling of goods, but also many services which must be provided to finance insure store and transport of goods in the course of these exchanges."
Thus, commerce is the process of buying and selling in which consist of warehousing, storin g, banking, insurance, grading, transportation, financing and packing.commerce also facilities in removing obstacles through trade,transportation, exchange, banking, place, time and advertisement and salesmanship.
g, banking, insurance, grading, transportation, financing and packing.commerce also facilities in removing obstacles through trade,transportation, exchange, banking, place, time and advertisement and salesmanship.
commerce main functions is to remove some of the hindrances as well as bridges the gap.
commerce removes such kind of hindrances they are as stated below:
- Of person: the producer and the consumers of goods and services are possible located at the same location. Trade, hence, bridges the gap between the marketer/producer and the consumers which helps to remove the hindrances. wholesalers and retailers help to established the contact between producers and the consumers by playing the role of mediator.
-Of exchange : here, Money plays great role as medium of exchange between producers and the customers. Due, money being a common means of exchange. In exchange between country financial institution like banks, financial companies remove the hindrances of exchange.
-Of place:company and customers aren't located at same place in this, transportation bridges the gap between producer and consumers to takes the products from place to place. here, packaging of the goods and services helps the lessen the damage, insurance lessen the risk of theft,fire,accident and warehousing works as storeroom in different places.
-Of information and knowledge: the main obstacles facing by producer today is selling goods and services produced by them even they produce quality goods and services and cost is reasonable though they are not cause due to lack of advertisement and salesman.
commerce also removes the hindrances of time and risk too. warehousing,cold stores and go downs protect them for future use.
Read full story
The structure of business refers to the components and parts of business comprising different classes of activities that it exercises. Business activities can be greatly classified in three classes they are as follows:industry,commerce and services.



INDUSTRY:
Industry refers to the production of goods through the utilization of various resources available in surroundings. Industry is the process of extracting production ,conversion, and fabrication of products by the use of human skills and mechanical power.
Industrial products are those used for further production of products. similarly, the goods used for further processing are called intermediate products such as semi-processed products.
Types of Industry
Generally, the industry is classified into two broad parts they are as follows:
Primary industry:
Primary industry is the basic industry whereby natural resources are consumed and living organisms and plants are reproduced. The role of nature is important in primary industry. The products of such industry are used by the secondary types of industry.

-Extractive industries: This type of industries are extractive from the nature like air, sea, earth, and soil with little application of human skills. Example of such industries are mining of gold and cold from the earth. fishing from sea or rivers, exaction of oil and gas from the oil wells risings crops from soil and climate and more.
Geneti
 c industries:the industries in which certain sp
c industries:the industries in which certain sp ecies of plants and animals are multiplied and reproduction for the purpose of creating of wealth is called genetic industries.some of the examples are as follows of genetic industries poultry farming; plants grown for sale; animal husbandry where cattle are raised for milk and leather and sheep's; orchards to harvest different kinds of fruits; commercial kennels and agriculture
ecies of plants and animals are multiplied and reproduction for the purpose of creating of wealth is called genetic industries.some of the examples are as follows of genetic industries poultry farming; plants grown for sale; animal husbandry where cattle are raised for milk and leather and sheep's; orchards to harvest different kinds of fruits; commercial kennels and agricultureSecondary Industries:
The Industries are which convert the raw materials and semi-processed materials into finished goods is known as Secondary industries. Secondary industries depends upon the outputs of the basic industries. Secondary industries
 can be categories into manufacturing and construction.
can be categories into manufacturing and construction.
Manufacturing industries:Manufacturing industries transform or convert raw materials into finished products. these industries create a from utility by converting raw materials into final products. Manufacturing industries example are iron and steel,automobile, machinery,electrical and electronics,sugar mills, textile mills, mechanical, etc.
Manufacturing industries is also divided into sub-parts they are as below:
Analytical industries: The industries which utilize analytic process in the

production of goods. Goods and services are manufactured by analyzing the raw materials and separates them to give or produce final products. for example;oils refineries which produces kerosene, diesel, aviation oil, petrol and lubricating.
Synthetic industries: Synthetic industries' are those type of production
 which uses synthetic while producing goods and final products. for example:- mixing of limestone,coal,clay,gypsum to formed cement.
which uses synthetic while producing goods and final products. for example:- mixing of limestone,coal,clay,gypsum to formed cement.Processing industries: such types of industries, raw

materials are processed through different phase of production to attend final products. the example of such industries is the raw jute passes through different stages of spinning, weaving, sewing and dyeing to produce jute products.
Assembling Industries:Assembling Industries are
 such industries where different components or parts
such industries where different components or partsalready manufactured by other companies and are
brought together and assemble to produce a final products.
for example automobile, radio, bicycle, watch,
computers,televisions.

continuous Industries: In such type of industries, all the needed
materials are insert into the machine at one point from which successive are automatically performed to turn them into a finished products. for example; Bhirkuti paper mill, Butwal spinning mill, lumbini sugar mill are the example of Nepal for continues types of manufacturing industries.
Construction Industries: The construction industries which are
involved in the construction of roads, bridges,culverts, building,
culverts and so on. for example such construction takes place at a
fixed site. Construction industries are of cement, concretes, steels,
irons and tar coal as raw materials.

COMMERCE: The process of exchanging goods and services is known as commerce.
In the words of James Stephenson,"Commerce is concerned with the exchange of goods with all that is involved in buying and selling of goods at any stage in their progress from raw materials to finished goods in the consumers' hands. It covers not only the function of buying ans selling and handling of goods, but also many services which must be provided to finance insure store and transport of goods in the course of these exchanges."
Thus, commerce is the process of buying and selling in which consist of warehousing, storin
 g, banking, insurance, grading, transportation, financing and packing.commerce also facilities in removing obstacles through trade,transportation, exchange, banking, place, time and advertisement and salesmanship.
g, banking, insurance, grading, transportation, financing and packing.commerce also facilities in removing obstacles through trade,transportation, exchange, banking, place, time and advertisement and salesmanship.commerce main functions is to remove some of the hindrances as well as bridges the gap.
commerce removes such kind of hindrances they are as stated below:
- Of person: the producer and the consumers of goods and services are possible located at the same location. Trade, hence, bridges the gap between the marketer/producer and the consumers which helps to remove the hindrances. wholesalers and retailers help to established the contact between producers and the consumers by playing the role of mediator.
-Of exchange : here, Money plays great role as medium of exchange between producers and the customers. Due, money being a common means of exchange. In exchange between country financial institution like banks, financial companies remove the hindrances of exchange.
-Of place:company and customers aren't located at same place in this, transportation bridges the gap between producer and consumers to takes the products from place to place. here, packaging of the goods and services helps the lessen the damage, insurance lessen the risk of theft,fire,accident and warehousing works as storeroom in different places.
-Of information and knowledge: the main obstacles facing by producer today is selling goods and services produced by them even they produce quality goods and services and cost is reasonable though they are not cause due to lack of advertisement and salesman.
commerce also removes the hindrances of time and risk too. warehousing,cold stores and go downs protect them for future use.




